NewsDetails
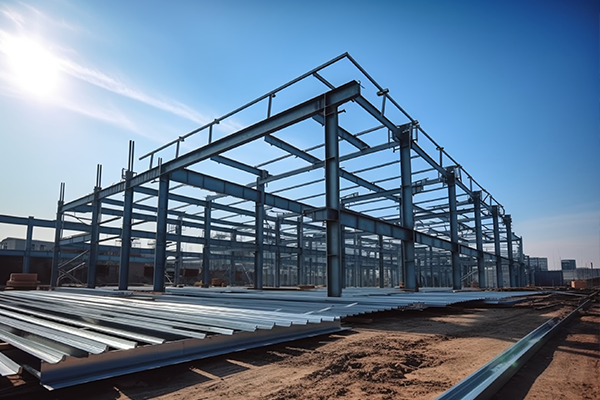
The role of Z-shaped steel
author:Tianxing time:2025-04-14 18:14:52 Click:53
1. Primary Functions of Z-Shaped Steel
(1) Roof & Wall Purlins
Supports cladding materials: Z-sections are widely used as purlins in light steel structures (e.g., supporting metal roofs or sandwich panels), bearing wind loads, snow loads, and self-weight.
Large-span advantage: Due to their high moment of inertia, Z-sections outperform C-sections in long spans (6–12 m), reducing intermediate supports and material costs.
(2) Continuous Lapped Connections
Enhanced integrity: Z-sections can be lapped to form continuous beams, improving overall stiffness and bending resistance (common in warehouses/factories).
(3) Wind & Seismic Resistance
Sloped flanges disperse lateral forces: The Z-shape helps distribute wind/seismic loads more effectively than C-sections.
(4) Industrial Equipment Frames
Used for light-duty platforms, conveyor supports, etc., due to easy installation and moderate load capacity.
2. Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High sectional efficiency | Z-profile offers superior bending resistance vs. C-sections for long spans. |
| Lapped connections | Overlapping flanges create continuous load paths, minimizing weak joints. |
| Lightweight | Cold-formed thin-walled design reduces structural weight. |
| Material savings | Lower steel consumption than traditional sections (e.g., I-beams) at equal strength. |
| Easy installation | Bolt-fastened, enabling rapid assembly. |
3. Z-Section vs. C-Section
| Aspect | Z-Section | C-Section |
|---|---|---|
| Profile | Zigzag "Z", bidirectional lapping | Open "C", unidirectional fixing |
| Bending resistance | Stronger, ideal for long spans (>6 m) | Weaker, suited for short spans (≤6 m) |
| Connection | Continuous lapping improves integrity | Requires individual joints |
| Applications | Large-span roofs, continuous purlins | Wall girts, light framing |
4. Typical Applications
Industrial buildings: Roof purlins for factories/warehouses.
Public facilities: Lightweight roofs (stadiums, exhibition halls).
Agricultural structures: Greenhouse frameworks.
Modular construction: Prefabricated housing.
5. Selection Considerations
Span: Choose Z-sections for spans >6 m; C-sections suffice for shorter spans.
Loads: Verify capacity against wind/snow loads (e.g., section size: Z200×70×20×2.0).
Corrosion protection: Galvanized Z-sections for humid/coastal environments.
Installation: Pre-design lapping details to avoid on-site cutting weakening the structure.
Conclusion
Z-shaped steel excels in large-span, lightweight structures (e.g., industrial roofs) due to its efficient profile, lapping flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Engineers should evaluate loads, spans, and budgets for optimal selection.
Let me know if you need further details!
 Recommended Products
Recommended Products
 Contact us
Contact us
—— Contact:Ms. Zhang
—— Tel:(+86)18399688883
—— Email:18399688883@163.com
—— Url:https://www.tianxingmaterials.com
—— Address:Horgos City, Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China